MITM Attack
MITM Attack
In this post you are going to learn, what is MITM attack, examples, phases, preventions & tools to perform MITM Attack.
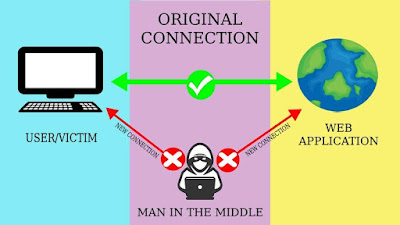
What is MITM Attack - A man-in-the-middle or person-in-the-middle (PITM) is a type of cyberattack where an attacker places himself between two users or computers and tries to intercept the data or alters the data or steals the data and forwards it to the sender/receiver.
One more form of MITM is MITB i.e. man-in-the-browser where in, an attacker places a bot in the browser to steal the details of the users and then sends it to an attacker.
Example - There are two users - A, B & there is an attacker in between them. User A asks user B to send public key of user B so that user A can encrypt the message and send it to the user B. User B sends it's public key to user A, since an attacker is in between them he gets the public key of user B and sends it's own public key to the user A.
User A thinks the public key he received is of user B so he sends the encrypted message to user B using an attacker's public key. Now an attacker receives the message before it reaches to the user B and decrypts the message using it's own public key and either he steals the message or alters the message and after reading the message he encrypts the message using user B's public key and forwards it to B.
None of them is aware about the violation of privacy occurring between their conversation. Hence successful MITM takes place in this manner.
Phases -
MITM consists of two phases - Interception & Decryption.
Interception - Here an attacker sniffs the data, captures the data, intercepts the data for its own purpose.
Methods to do interception -
- IP Spoofing
- ARP Poisoning
- DNS Poisoning
Decryption - Since data transmission takes place in an encrypted form, the data needs to be decrypted without alerting user or application.
Methods to do decryption -
- HTTP Poisoning
- SSL Hijacking
- SSL Stripping
- SSL Beast
Prevention -
1. Keeping an eye on browser's protocol whether it is secured or not secured.
2. Not connecting to the WIFI having no password protection.
3. Not using public networks while transmission of sensitive information.
4. Paying attention to browser's notifications.
Tools -
1. Ettercap
2. DSniff
3. PacketCreator
Learn : DNS


Comments
Post a Comment